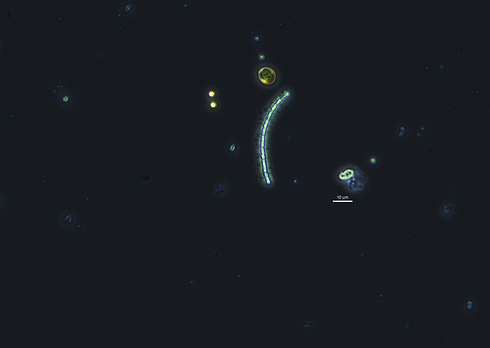
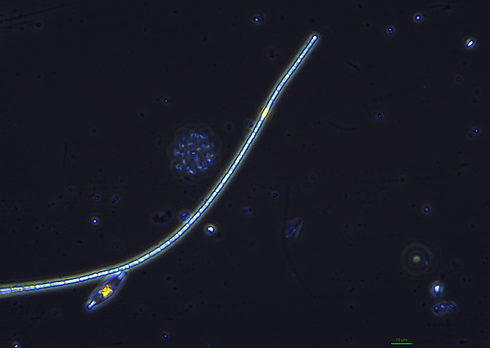
Pseudanabaena sp.
Key to Families
1. Cells growing to the original size of the mother cell before the next division.......................... 2
1: Cells not growing to the original size before division; divisions occurring in rapid succession............5
2. Trichomes fragmenting with necridia into motile hormogonia (1)............................................... PHORMIDIACEAE
2: Trichomes fragmenting usually without necridia............................................................................3
3. Trichomes with a widened sheath enveloping several to many trichomes (2:)............................ SCHIZOTRICHACEAE
3: Trichomes generally lacking a well-developed sheath, although thin delicate sheaths may be present in some genera.........4
4. Trichomes very short, usually few-celled, sometimes moniliform; cells isodiametric, broadly cylindrical to +-spherical (3:)..............BORZIACEAE
4: Trichomes usually more than a few cells long; cells cylindrical, +-isodiametric or mainly longer than wide........... PSEUDANABAENACEAE
5. Trichomes oval, arcuate or triangular in cross-section (1:)....................................... GOMONTIELLACEAE
5: Trichomes circular in cross-section......................................... OSCILLATORIACEAE
Key to genus
1. Trichomes heteropolar, always attached to the substratum at one end................... HETEROLEIBLEINIA
1: Trichomes isopolar, sometimes attached to the substratum along the length (or part) of the filament..........2
2. Trichomes regularly spirally coiled, without a sheath (1:)......... SPIRULINA
2: Trichomes straight, flexuous or variously coiled, with or without a sheath.......3
3. Trichomes planktonic, delicate; sheath extending beyond the trichome at both ends (2:)........ PLANKTOLYNGBYA
3: Trichomes benthic or metaphytic or planktonic; sheath, if present, not extending beyond the trichome at both ends.......4
4. Trichomes with or without a sheath (3:)............5
4: Trichomes always without a sheath...................6
5. Trichomes epiphytic, delicate, solitary, attached to the substratum along their entire length or with the ends free (4)...... LEIBLEINIA
5: Trichomes forming a tightly tangled mat............... LEPTOLYNGBYA
6. Cells clearly constricted at the cross-walls (4:)............7
6: Cells usually not constricted at the cross-walls...........8
7. Trichomes small, filamentous or pseudofilamentous, few-celled, arcuate or irregularly curved or coiled screw-like (6)..... ROMERIA
7: Trichomes solitary, generally straight; cells isodiametric or mainly longer than wide............. PSEUDANABAENA
8. Cells containing polar or central aerotopes (6:)............. LIMNOTHRIX
8: Cells without aerotopes.............9
9. Cell contents generally uniform, rarely with prominent granules (8:)................. JAAGINEMA
9: Cells containing large cyanophycin granules or conspicuous localised carotenoid bodies...... GEITLERINEMA
Key to Species
1. Trichomes very short (3-5 celled)............................................................................2
1: Trichomes longer........................................................................................................3
2. Apical cell rounded, usually within the mucilage of other colonial cyanoprokaryotes (1).......P. mucicola
2: Apical cell elongate, conically narrowed and sharply pointed............................P. franquetii
3. Trichomes > 3.0 um wide; cells 2 times longer than wide (1:)..............................Pseudanabaena sp. A
3: Trichomes < 3.0 um wide...........................................................................................4
4. Cells with large aerotopes on either side of cross-walls, 2.5-5.0 (-7.0) long, (1.5-) 1.7-2.0 um wide (3:)....P. amphigranulata
4: Cells without aerotopes on either side of cross-walls............................................5
5. Cells abutting each other, constricted at the cross-walls (4:).................................P. limnetica
5: Cells separated by hyline bridges................................................................................6
6. Apical cell cylindrical, with rounded end; cells 2-4um long, 1.2-2.0 um wide (5:)..P. catenata
6: Apical cell slightly conical or rounded at the apex, with 1 or more aerotopes, often ring or dome-shaped, sometimes appearing as an apical protrusion; cells 1.5-7.5um long...............P. galeata

Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project

Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project

