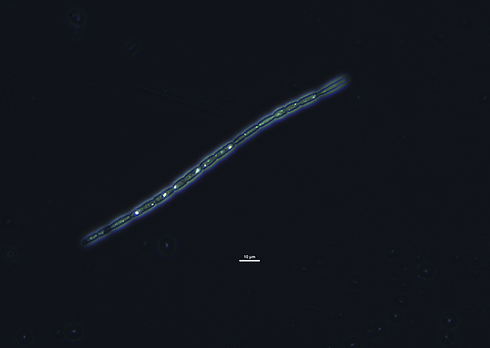
Chrysosporum sp.
KEY TO FAMILIES
1. Filamentous, heterocystous, isopolar, with free uniseriate trichomes enveloped by fine mucilaginous envelopes or sheaths.
Filaments ± straight, flexuous, or ± irregularly screw-like coiled, without branching; all vegetative cells capable of cell division.
Vegetative cells spherical, barrel-shaped to cylindrical, apical cells rounded, conical, acutely pointed or cylindrical and bluntly
rounded, with or without aerotopes. Heterocytes terminal or intercalary. Akinetes often several times larger than vegetative cells,
formed from one vegetative cell or from the fusion of several vegetative cells, positioned adjacent or remote from heterocytes
..............................................................................................................................................................1. APHANIZOMENONACEAE
(Genera included in this volume: Anabaenopsis, Aphanizomenon, Chrysosporum, Cuspidothrix, Dolichospermum, Nodularia,
Raphidiopsis, Sphaerospermopsis)
KEY TO GENERA
1. Trichomes always without heterocytes.......................................................................................................................RAPHIDIOPSIS
- Trichomes capable of producing heterocytes......................................................................................................................................2
2. Heterocytes terminal.............................................................................................RAPHIDIOPSIS (in part, ex. Cylindrospermopsis)
- Heterocytes intercalary........................................................................................................................................................................3
3. Heterocytes develop in pairs which, following trichome breakage, are in the terminal position.......................... ANABAENOPSIS
- Heterocytes solitary.............................................................................................................................................................................4
4. Apical cells generally differentiated, elongated, tapered, or hyaline..................................................................................................5
- Apical cells generally undifferentiated................................................................................................................................................6
5. Apical cells elongated, attenuated and acuminate................................................................................................... CUSPIDOTHRIX
- Apical cells conical, or tapered and elongated, often hyaline..............................................................................CHRYSOSPORUM
6. Vegetative cells always distinctly shorter than broad....................................................................................................NODULARIA
- Vegetative cells ± isodiametric or longer than wide............................................................................................................................7
7. Akinetes spherical, always developing either side of the heterocytes........................................................ SPHAEROSPERMOPSIS
- Akinetes adjacent to or remote from heterocytes................................................................................................................................8
8. Akinetes long cylindrical, often with a collar-like extension at either end which extends over the adjacent vegetative cells.............
.............................................................................................................................................APHANIZOMENON (in part A. gracile)
- Akinetes oval to cylindrical.............................................................................................................................DOLICHOSPERMUM
KEY TO SPECIES
Filaments planktonic; trichomes solitary, straight or slightly flexuous, constricted at the cross walls. Apical cells conical,
or tapered and elongated, often hyaline. Vegetative cells cylindrical, compressed during division, with aerotopes.
Heterocytes intercalary, solitary, spherical, or slightly elongated. Akinetes widely ovoid, with brownish or yellowbrown
epispore, remote from heterocytes.
A widely distributed genus of three species, all known from the plankton of freshwater lakes, reservoirs and rivers.
Here two species are described from north-eastern Australia. Bibliography: Baker (1991), Stüken et al. (2006, 2009),
Komárek & Mareš (2012), Zapomělová et al. (2012), Sukenik et al. (2012), Komárek (2016).
1. Vegetative cells barrel-shaped, 4–8 μm broad, apical cells conically narrowed and tapered.................................................C. bergii
- Vegetative cells cylindrical, 2.5–4.5 μm broad, apical cells elongated, narrowed and hyaline ..................................C. ovalisporum


Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project

Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project


Project
Project

